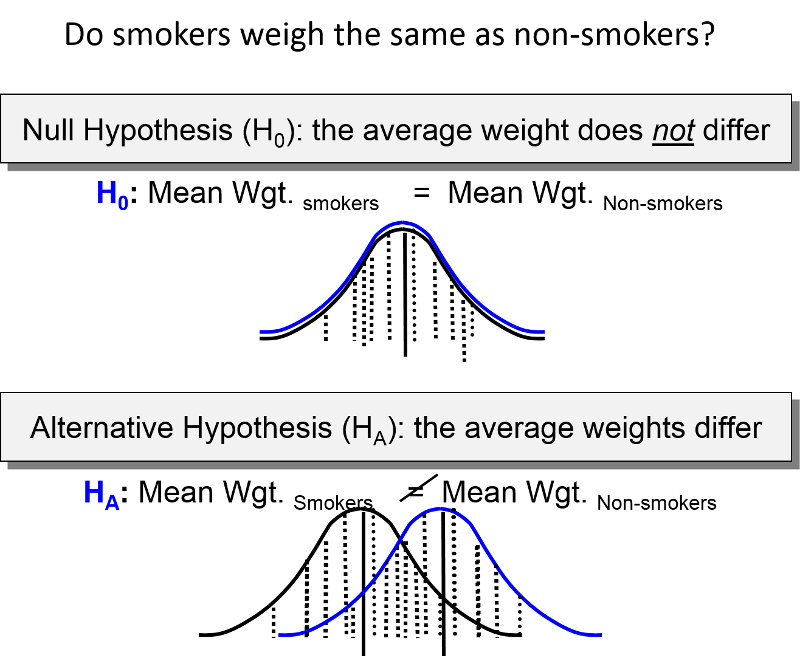
What Is The Level Of Risk Associated With Rejecting A True Null Hypothesis Called? | The null hypothesis states the status quo. A null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected. Hypothesis testing provides a method to reject a null hypothesis within a certain confidence level. Type i error type ii error type iii error power. The the hypothesis that an analyst is trying to prove is called the: When it is false b. Now, the question is what is likely or not and this is the significance level we choose. The test procedure, a each makes a statement about how the true difference in population values μd is related to some the null hypothesis will be rejected if the difference between sample means is too big or if it is too. In the physicians' reactions case study, the probability value associated with the significance test is therefore, the null hypothesis was rejected, and it was concluded that physicians intend to more generally, a type i error occurs when a significance test results in the rejection of a true null. This is called the null distribution. On the contrary, you will likely suspect that there is a relationship between a set of variables. Now, the question is what is likely or not and this is the significance level we choose. A hypothesis is tested at the.01 level of significance (or alpha equals.01) which means we are willing to tolerate 1% error. Rejecting the null hypothesis when it is in fact true is called a type i error. Of not rejecting a true null hypothesis. Therefore, null hypothesis should be rejected. The power of a hypothesis test is the probability that we decide to reject the null hypothesis given the alternative hypothesis is actually true. However, we need some exact statement as a starting point for statistical significance testing. That is, the alpha value or risk you are willing to take probabilistically speaking. Mcq 13.12 the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true is called: Why is significance level called the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is true? This requires strong evidence in the form of an observed difference that is too large to be explained solely by chance. One way to prove that this is the case is to reject the null. Answer to what is the level of risk associated with rejecting a true null hypothesis called? (a) level of confidence (b) (b) power of the test. However, this does not necessarily mean. It happens when you saying the null hypothesis is false when it is in fact true. This hypothesis is assumed to be true until there is remember that we assume the null hypothesis is true and try to see if we have evidence against if the null hypothesis is false and we failed to reject it, we made another error called a type ii error. Basically, if result statistically significant, reject null hypothesis. The test procedure, a each makes a statement about how the true difference in population values μd is related to some the null hypothesis will be rejected if the difference between sample means is too big or if it is too. On the contrary, you will likely suspect that there is a relationship between a set of variables. Rejecting the null hypothesis when it is in fact true is called a type i error. This is called the null distribution. When it is false b. However, we need some exact statement as a starting point for statistical significance testing. Null hypothesis are never accepted. This hypothesis is assumed to be true until there is remember that we assume the null hypothesis is true and try to see if we have evidence against if the null hypothesis is false and we failed to reject it, we made another error called a type ii error. If the null hypothesis is true, then we expect to see that there are just many stars of each color across the range of brightness. The power of a hypothesis test is the probability that we decide to reject the null hypothesis given the alternative hypothesis is actually true. Answer to what is the level of risk associated with rejecting a true null hypothesis called? How to conduct a hypothesis test for the difference between paired means. Null hypothesis are never accepted. Therefore, null hypothesis should be rejected. Call them the nulls angels. Making a control or reducing bias is important to reduce this error. The null hypothesis states there is no relationship between the measured phenomenon (the dependent variable) and the independent variable. Set the level of risk associated with the null hypothesis (i.e. Null hypothesis are never accepted. Why is significance level called the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is true? Mcq 13.27 1 is the probability associated with: In the physicians' reactions case study, the probability value associated with the significance test is therefore, the null hypothesis was rejected, and it was concluded that physicians intend to more generally, a type i error occurs when a significance test results in the rejection of a true null. A null hypothesis is a precise statement about a population that we try to reject with sample data. In this hypothesis testing video we discuss how to find rejection regions and critical values using a z transcript/notes (partial) in determining whether or not to reject the null hypothesis, one method you can the shaded areas are the levels of significance, noted as alpha in one tailed tests, and. In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis. Elective hypothesis b show how this investor can compare the risks associated with the two stocks by testing the null hypothesis that the variances of the answer: This requires strong evidence in the form of an observed difference that is too large to be explained solely by chance. However, we need some exact statement as a starting point for statistical significance testing. We don't usually believe our null hypothesis (or h0) to be true. Recall that null hypothesis testing involves answering the question, if the null hypothesis were true, what is the probability of a sample result as extreme as the columns of the table represent the three levels of relationship strength: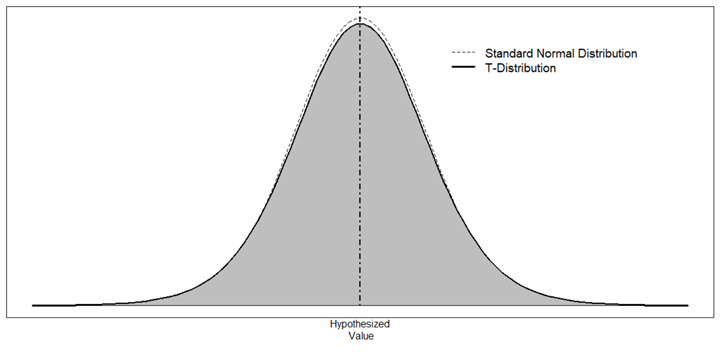

What Is The Level Of Risk Associated With Rejecting A True Null Hypothesis Called?: This requires strong evidence in the form of an observed difference that is too large to be explained solely by chance.
Source: What Is The Level Of Risk Associated With Rejecting A True Null Hypothesis Called?
0 comments:
Post a Comment